Radio frequency identification (RFID) is widely used in logistics management, transportation management, and factory production control because of its long distance recognition and other characteristics. This article will introduce a software radio-based RFID reader design that addresses the need to purchase a different reader to read and write different types of RFID tags.
For the current RFID system operating frequency is diverse, various types of standards are numerous and there is a large gap, not suitable for the simultaneous application of a variety of labels, the idea of ​​designing an RFID reader based on software radio and Lab VIEW is proposed. By loading different software codes, the emulation reader can read and write RFID tags of different frequency bands and meet different standards. Comparing with the reading result of the standard reader, the emulation reader realizes the reading of the information carried by the RFID tag, and saves the cost of configuring various types of readers.
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a technology that uses the spatial coupling and backscattering characteristics of RF signals to automatically identify and exchange data with target objects. Therefore, the recognition process does not require manual intervention, and has the characteristics of high precision, long life, and easy operation.
UHF RFID has been used more and more in logistics management, transportation management, and factory production control because of its long distance recognition. Currently, RFID standards are complex and there is no universal application standard. Therefore, for applications with a wide variety of tags and RFID technology research and development institutes, it is necessary to develop a reader that can support multiple RFID tag standards. Using software radio features, different RFID standards are implemented in software code. Through the method of loading different software codes, read and write operations are performed on RFID tags that comply with different standards. It can easily solve the problem of needing to buy different readers to read and write different types of RFID tags.
Software radio is a brand-new design idea that gradually emerged after the 1990s. Its core is the universal modularization. The programmable hardware platform loads different communication software to realize the conversion between different communication modes. This design idea makes the radio station in communication adapt to different communication methods. The good compatibility and programmability of the software radio make the development of the communication system become the research of digital signal processing software. Based on this idea, various RFID standards can be attempted to be implemented in the form of software codes, so as to achieve the function of an RFID reader complying with various standards by loading different software.
This article uses Lab VIEW software developed by NI company to write the code of software radio. Lab VIEW is one of the most widely used data acquisition and control development environments in the world. It has an important role in the field of communication simulation. It uses a graphical programming language (also known as the "G" language) to program, and the resulting program is in the form of a block diagram. Lab VIEW is also a general-purpose programming system that has a large library of functions for any programming task, including data acquisition, GPIB, serial port control, data analysis, data display, and data storage. It can enhance the ability of research and development staff to build their own science and engineering systems, and provide an easy way to implement instrument programming and data acquisition systems.
1. Software Radio-based RFID Reader Model
To reflect the RFID tag back to the information it carries, it is necessary to first obtain the excitation signal, and then the voltage regulator transmits the RF signal transmitted from the reader to a DC stabilized power supply. So we need the software radio (emulation reader) to launch the excitation wave first. In some of the more secure RFID application protocols, it also includes the process of safety certification and operation of the tag, which requires adding some operation instruction codes to the excitation wave. Get the corresponding information from the tag. The reflected signal of the tag carries its own information. During the reception of the reflected signal, the channel fades. The multipath effect, plus the receiver itself, also introduces noise. Therefore, these effects need to be filtered before the information is parsed. The emulation reader uses co-frequency demodulation with the same carrier frequency as the excitation wave. The entire RFID simulation reader framework is shown in Figure 1.
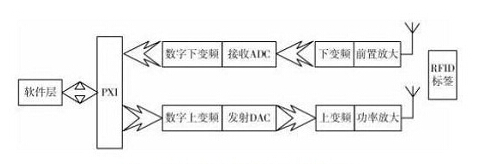
Software Radio Reader System Framework
2, the analysis of tag information
This article reads AARS-918-compliant RFID tags. The standard specifies the operating frequency, transmission/reception bandwidth, modulation method, transmitter power, and coding scheme of the RFID system.
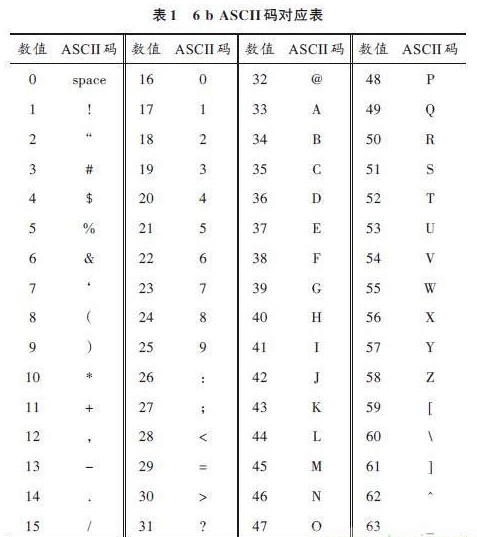
The coding scheme is shown in Fig. 2. It can be seen from Fig. 2 that each user data bit is replaced with 8 sub bits, that is, the user data "1" is replaced with "10101100", and the user data "0" is used. 11001010" instead. The data frame identifier is "1010101010101100". Filter the reflected signal on the tag. After demodulation and other signal processing, the original baseband signal is restored. Next, restore the tag-carrying information. The AARS-918 standard uses the unique 6bASCII encoding. The correspondence between the encodings is shown in Table 1.
3, reader performance testing
According to the working principle of the RFID system and the AARS-918 standard for the frequency of the work, first use the Lab VIEW software to program the launch excitation wave, set the carrier frequency to 915MHz, the sampling rate is 800kHz, and the transmission gain is 30dB. The program front panel and system block diagram are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
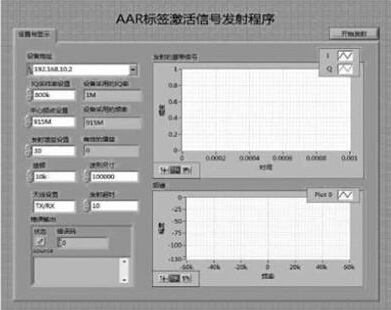
Tag stimulus signal launcher
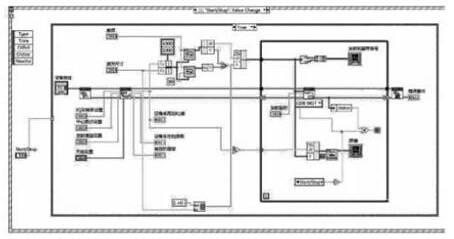
Block diagram of excitation signal
When the tag enters the identification area of ​​the reader, the information it carries will be transmitted back to the reader through electromagnetic reflection. The emulated reader demodulates the reflected ASK signal according to the AARS-918 standard specification and according to AARS. The coding rules of the -918 standard are used to decode the information it carries. The signal processing and decoding procedures of the reader are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6.
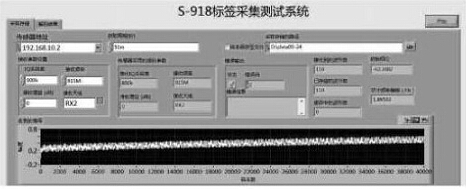
Label reflection signal collection

Analysis of tag information
As can be seen from Figure 6, after parsing, the information carried by the tag is "$1 (B, S1$). The data read by the standard commercial reader is shown in Figure 7. As can be seen from Figure 7, The data read by the reader is exactly the same as the data read by the emulation reader, and the emulated reader successfully reads the information carried by the tag itself and implements the functions of a standard reader.
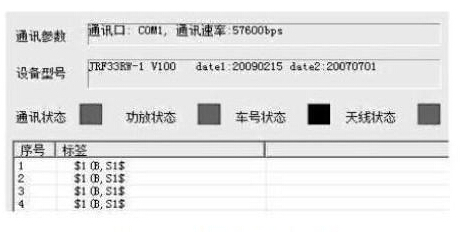
Standard reader reads the result
4 Conclusion
This article through the study of software radio and RFID systems, using the Lab VIEW graphical programming language to design a software-based radio RFID reader. By comparing with the reading results of a standard reader, this design enables the reading function of a standard reader. Thus, the function of reading and writing RFID tags complying with different standards by loading different software is realized, and is suitable for occasions where multiple different standards of tags are applied at the same time.
The AARS-918 standard targeted by this article can be implemented more simply because it does not have a complex protocol authentication process. In future work, other protocol standards will be studied and added to the code base to facilitate the implementation of loading and unloading RFID tags.
For the current RFID system operating frequency is diverse, various types of standards are numerous and there is a large gap, not suitable for the simultaneous application of a variety of labels, the idea of ​​designing an RFID reader based on software radio and Lab VIEW is proposed. By loading different software codes, the emulation reader can read and write RFID tags of different frequency bands and meet different standards. Comparing with the reading result of the standard reader, the emulation reader realizes the reading of the information carried by the RFID tag, and saves the cost of configuring various types of readers.
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a technology that uses the spatial coupling and backscattering characteristics of RF signals to automatically identify and exchange data with target objects. Therefore, the recognition process does not require manual intervention, and has the characteristics of high precision, long life, and easy operation.
UHF RFID has been used more and more in logistics management, transportation management, and factory production control because of its long distance recognition. Currently, RFID standards are complex and there is no universal application standard. Therefore, for applications with a wide variety of tags and RFID technology research and development institutes, it is necessary to develop a reader that can support multiple RFID tag standards. Using software radio features, different RFID standards are implemented in software code. Through the method of loading different software codes, read and write operations are performed on RFID tags that comply with different standards. It can easily solve the problem of needing to buy different readers to read and write different types of RFID tags.
Software radio is a brand-new design idea that gradually emerged after the 1990s. Its core is the universal modularization. The programmable hardware platform loads different communication software to realize the conversion between different communication modes. This design idea makes the radio station in communication adapt to different communication methods. The good compatibility and programmability of the software radio make the development of the communication system become the research of digital signal processing software. Based on this idea, various RFID standards can be attempted to be implemented in the form of software codes, so as to achieve the function of an RFID reader complying with various standards by loading different software.
This article uses Lab VIEW software developed by NI company to write the code of software radio. Lab VIEW is one of the most widely used data acquisition and control development environments in the world. It has an important role in the field of communication simulation. It uses a graphical programming language (also known as the "G" language) to program, and the resulting program is in the form of a block diagram. Lab VIEW is also a general-purpose programming system that has a large library of functions for any programming task, including data acquisition, GPIB, serial port control, data analysis, data display, and data storage. It can enhance the ability of research and development staff to build their own science and engineering systems, and provide an easy way to implement instrument programming and data acquisition systems.
1. Software Radio-based RFID Reader Model
To reflect the RFID tag back to the information it carries, it is necessary to first obtain the excitation signal, and then the voltage regulator transmits the RF signal transmitted from the reader to a DC stabilized power supply. So we need the software radio (emulation reader) to launch the excitation wave first. In some of the more secure RFID application protocols, it also includes the process of safety certification and operation of the tag, which requires adding some operation instruction codes to the excitation wave. Get the corresponding information from the tag. The reflected signal of the tag carries its own information. During the reception of the reflected signal, the channel fades. The multipath effect, plus the receiver itself, also introduces noise. Therefore, these effects need to be filtered before the information is parsed. The emulation reader uses co-frequency demodulation with the same carrier frequency as the excitation wave. The entire RFID simulation reader framework is shown in Figure 1.

Software Radio Reader System Framework
2, the analysis of tag information
This article reads AARS-918-compliant RFID tags. The standard specifies the operating frequency, transmission/reception bandwidth, modulation method, transmitter power, and coding scheme of the RFID system.
The coding scheme is shown in Fig. 2. It can be seen from Fig. 2 that each user data bit is replaced with 8 sub bits, that is, the user data "1" is replaced with "10101100", and the user data "0" is used. 11001010" instead. The data frame identifier is "1010101010101100". Filter the reflected signal on the tag. After demodulation and other signal processing, the original baseband signal is restored. Next, restore the tag-carrying information. The AARS-918 standard uses the unique 6bASCII encoding. The correspondence between the encodings is shown in Table 1.


3, reader performance testing
According to the working principle of the RFID system and the AARS-918 standard for the frequency of the work, first use the Lab VIEW software to program the launch excitation wave, set the carrier frequency to 915MHz, the sampling rate is 800kHz, and the transmission gain is 30dB. The program front panel and system block diagram are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.

Tag stimulus signal launcher

Block diagram of excitation signal
When the tag enters the identification area of ​​the reader, the information it carries will be transmitted back to the reader through electromagnetic reflection. The emulated reader demodulates the reflected ASK signal according to the AARS-918 standard specification and according to AARS. The coding rules of the -918 standard are used to decode the information it carries. The signal processing and decoding procedures of the reader are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6.

Label reflection signal collection

Analysis of tag information
As can be seen from Figure 6, after parsing, the information carried by the tag is "$1 (B, S1$). The data read by the standard commercial reader is shown in Figure 7. As can be seen from Figure 7, The data read by the reader is exactly the same as the data read by the emulation reader, and the emulated reader successfully reads the information carried by the tag itself and implements the functions of a standard reader.

Standard reader reads the result
4 Conclusion
This article through the study of software radio and RFID systems, using the Lab VIEW graphical programming language to design a software-based radio RFID reader. By comparing with the reading results of a standard reader, this design enables the reading function of a standard reader. Thus, the function of reading and writing RFID tags complying with different standards by loading different software is realized, and is suitable for occasions where multiple different standards of tags are applied at the same time.
The AARS-918 standard targeted by this article can be implemented more simply because it does not have a complex protocol authentication process. In future work, other protocol standards will be studied and added to the code base to facilitate the implementation of loading and unloading RFID tags.
Traffic And Transportation DFC system
Subway gate Subway seat High-speed train door are common traffic transportation tools. Their grinding processing at present are manual, the force imposing on the Grinder is not consistent, most are based on technician experience or technique. Our Force Control System can flexible control the force imposing on the grinder, quick response to the surface changing, and instant adjusting the force on the grinder.
Subway gate DFC system,Subway seat DFC system,High-speed train door DFC system
DARU Technology (Suzhou) Co., Ltd. , https://www.yiwufizz.com